The Now -
What is Machine Learning?

The Now
What is Machine Learning?


/en/thenow/what-are-genetically-modified-organisms-gmos/content/
As technology continues to evolve and the world's population continues to grow, so does the amount of data being generated. Collecting, sorting, and analyzing this data can be a pretty time-consuming task. However, that's all beginning to change with the emergence of machine learning, a type of computer science that allows computer programs to learn and improve on their own.
Watch the video below to see examples of how machine learning is used today.
In the past, computers were only able to do what we programmed them to do. But with machine learning, we can create software that learns in a similar way to humans: It gains knowledge based on past experience. Instead of having to constantly update the code of this software, it's able to improve its own performance as time goes by.
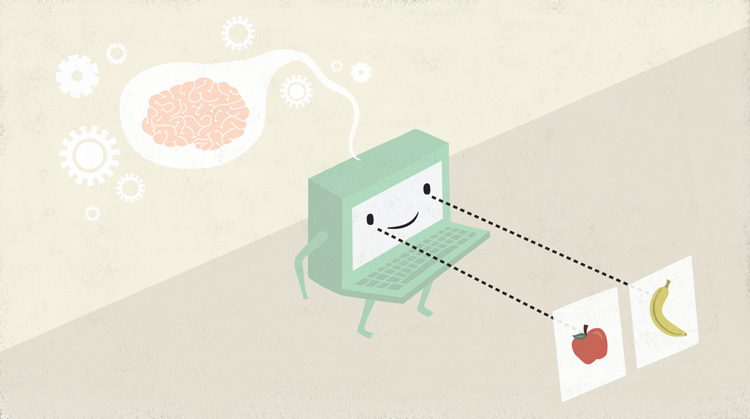
Machine learning can get pretty complicated, but here's how it works on a basic level. Let's say we want a program that can tell the difference between pictures of apples and bananas. We first give it a few labeled examples of each, and it looks for patterns in both fruits and remembers them. It then uses these memories to look at unlabeled pictures of apples and bananas to determine what they are without outside help.
Watch this video from Oxford Sparks for a more in-depth look at how machine learning works.
Whether or not you realize it, you probably use machine learning on a daily basis, or are at least aware of technologies that use it. Below is a list of some examples found in popular apps and devices:
The medical industry is also experimenting with a variety of applications, including predicting life spans, organizing patient data, and even diagnosing certain diseases. By gathering data like X-rays, genetic profiles, and blood tests, computers may be able to diagnose specific ailments more quickly and confidently.
The business world has begun to incorporate machine learning into its practices as well. Some companies are already using chatbots with machine learning capabilities to improve their customer service functions. There's also the potential for sorting incoming support tickets for a faster response rate, as well as speeding up hiring processes by evaluating applications and resumes at a faster pace.
Other parties are simply experimenting with machine learning to see what they can make. You may have heard the term neural network thrown around recently; this is a specific type of machine learning technology that individuals have used to create interesting projects like the popular Deep Dream and these computer-generated recipe names.
While these numerous advances seem positive, there's also a rising concern as to whether machine learning will eliminate jobs. This depends on the industry, but it does have the potential to get rid of or dramatically change a variety of jobs, including drivers, bankers, and potentially even certain doctors.
Others have voiced concerns about the ethics of machine learning and how it has the potential to invade your privacy. For example, it wouldn't be difficult for someone to create a program that gathers your texts or instant messages and then poses as you in a conversation with someone else. While machine learning can be a very powerful tool, it's important to be aware of its possible negative effects as well.
/en/thenow/understanding-facial-recognition/content/